Network Transformation - Driven by Disaggregation
By: Neeraj Patel

The telecom industry is undergoing another major network transformation. While the transformation of TDM to IP has ushered in innovation, mobile operators and broadband service providers are now struggling to keep up with bandwidth and performance demands of a massive number of connected devices—and with user expectations for digital service experience.
According to Strategy Analytics’ May 2019 report “IoT Strategies, Connected Home Devices, Connected Computing Devices, Wireless Smartphone Strategies, Wearable Device Ecosystem, Smart Home Strategies” there were 22 billion devices connected to the Internet by the end of 2018, with predicted growth to 38.6 billion connected devices by 2025 and 50 billion by 2030. At the same time, mobile operators and broadband service providers must seek to reduce costs while overall ARPU (average revenue per user) growth continues to slow down or remain flat.
As such, these service providers are increasingly looking to disaggregate their networks in order to leverage a growing ecosystem of open software and hardware components from a multi-vendor ecosystem to reduce CapEx costs, to accelerate time to market, and to monetize new service introduction. The traditional model of sourcing proprietary and expensive equipment from a single, monolithic vendor doesn’t hold up in this new telecom world. Next-generation networks must be disaggregated, open, virtualized, and flexible enough to support demand while also enable new business efficiencies and economies.
Open Ecosystems—Drivers of Disaggregation
There are a number of open ecosystem organizations that have emerged to drive this disaggregation for both mobile Radio Access Networks (RAN) and fixed broadband access networks.
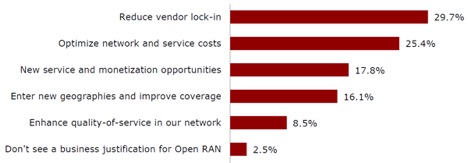
Figure 1 - Business justification for Open RAN initiatives.
Source: Heavy Reading’s 2018 Open RAN Operator Survey
For 4G and 5G RAN, the O-RAN Alliance is driving disaggregation through the delivery of open reference architectures and standardized interfaces that align with its core principles of openness and intelligence. The O-RAN Alliance is a mobile operator-led initiative with broad support from the global vendor community. It has many working groups, including the Stack Reference Design Workgroup (WG8) co-chaired by Radisys and Intel. This working group is focused on providing fully operable multi-vendor profile reference specification and interface documentation. The O-RAN Alliance’s Test and Infrastructure Group is tasked with delivering end-to-end test specifications to help drive interoperability in a multi-vendor ecosystem.
The Telecom Infra Project (TIP) was founded to accelerate the pace of innovation in telecom and it supports projects for the access network, transport, and core. In addition to disaggregation, its driving principle is to simplify the network. On the RAN side, this translates into initiatives that are focused on enabling simplified, flexible, and efficient RAN technologies that are commercially deployable.
Disaggregation is critical to the Open RAN evolution, as it enables mobile operators to truly open their radio infrastructure—the last part of the network to embrace “open”—to leverage solutions from multiple vendors. Heavy Reading’s recent report “2018 Open RAN Operator Survey” found that a majority of global mobile operator respondents believe that Open RAN is strategic to their business over the next three years (Figure 1, above). The primary business benefit cited by mobile operators for transitioning to Open RAN was to reduce vendor lock-in, followed closely by optimizing network and service costs. Disaggregation is critical for these benefits to be realized. In fact, only 2.5 percent of all global operators surveyed did not see Open RAN as a critical business strategy.