Understanding M-CORD: Re-architecting Mobile Infrastructure for 5G Services
M-CORD delivers three key capabilities for next-gen 5G networks:
- Enhanced resource utilization. An M-CORD infrastructure can improve compute resource utilization and deliver real-time analytics to extract intelligent information from the network and adjust resource utilization accordingly.
- Delivery of customized services for subscribers. Service providers will be able to create differentiation to enable various use cases for specific end users and respond in real time to end user demand. With an M-CORD infrastructure that can process local traffic at the edge, service providers could support high-bandwidth applications such as bringing premium video to mobile subscribers on demand as well as applications that require extremely low latency such as mobile gaming, virtual reality, connected cars, telematics and more.
- Agile and cost-efficient deployment. M-CORD supports on-demand deployment, a virtualized and disaggregated EPC and RAN, and commodity hardware and open source software.
Infrastructure Basics
M-CORD provides an open and flexible reference architecture to unify network and service orchestration through an open source software stack and commodity servers networked together with a leaf and spine fabric using white box switches. Service providers gain the benefit of choosing heterogeneous sets of open software and commodity hardware components, achieving a multi-vendor environment without the constraints of vendor lock-in.
In the case of EPC, M-CORD enables seamless interoperability between SDN controller interfaces and EPC elements such as a Packet Gateway and Serving Gateway, as disaggregated control and data plane services to deliver dynamic and flexible flow programmability. M-CORD allows for:
- Interoperability and integration testing of multi-vendor elements in the LTE networks;
- Enhancement of the LTE Packet Data Network Gateway (PGW) software to support control and data plane separation, enabling more dynamic and independent scale out management;
- Integration of disaggregated PGW components with the ONOS open SDN software platform, thus enabling increased network efficiency, programmability and elasticity in the LTE network; and
- PGW service composition with the XOS service orchestration environment for CORD, advancing service-driven mobile edge infrastructure as a critical path in the 5G architecture.
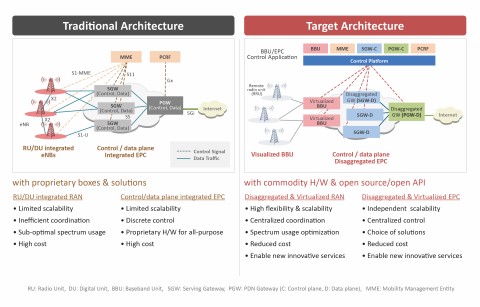
Figure 2 below shows a traditional network architecture composed of proprietary boxes and solutions and a target M-CORD architecture composed of commodity hardware and open source components to deliver a disaggregated/virtualized RAN and EPC.
Figure 2: Disaggregation/Virtualization of the RAN and EPCv
(click image to expand)