Mobile Networks: Navigating the Perfect Storm
Growing Mobile Network Complexity
3G and 4G radio access networks, and the associated IP-based networks, are increasing in complexity. In 3G Networks, Iub congestion is the cause for the majority of outages or degradations. ATM is used to carry voice and data from cell sites to switching centers. The ATM Adaption Layer 2 (AAL2) and ATM Adaption Layer 5 (AAL5) carries control and user information. Depending on the volume of traffic per service or RAB (radio access bearer), certain QoS could be congested at the AAL2. All Radio Access Bearers are configured to use Class A or Class B. These are mostly impacted by congestion. Most of the time Class B is the first QoS to get congested leading to failures. After admission events, Iub congestion could also be caused by misconfiguration of AAL2 profile at the Node B or Radio Node Controller (RNC).
The Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) plays a crucial role in enabling signaling in both 3G and 4G networks. Advanced devices and applications are consuming more signaling resources and affecting signaling plane throughput. Meanwhile increasing numbers of connected devices and base stations limit scalability because each connection requires significant signaling capacity. It is important that SCTP configurations are properly tuned in order to achieve optimal performance. In 3G networks, Iub congestion is often caused by route flapping in the IP backhaul network. This has been linked to different elements being set with different SCTP parameters. A mismatch will cause unnecessary retransmission, which will cause congestion during high-volume traffic. This type of error will only occur under high traffic and would not be detected until network performance and customer experience is impacted, or unless a network data configuration audit has been performed.
Analysis Service Provider Configuration Data
Data analysis from Nakina’s work with a national mobile operator suggests that network configuration issues contribute significantly to operational costs and impaired network performance. Serving approximately 40 million 3G mobile subscribers, the operator maintains a network of approximately 10,000 NodeBs and from approximately 5000 mobile towers. Each macrosite serves on average approximately 4000 mobile subscribers. On average, two NodeBs share the same tower, and so 5000 cell site routers (CSRs) are deployed for backhaul to radio node controllers (RNCs). Approximately 150 backhaul aggregation carrier Ethernet switch routers (CESRs) are used to aggregate backhaul traffic from the 5000 CSRs. The mobile operator has implemented approximately 135 RNCs network-wide, each supporting approximately 75 NodeBs.
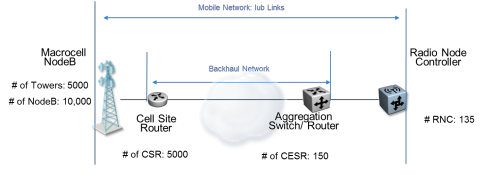
Nakina’s NI-CONTROLLER network data integrity and analytics solution audits close to 10,000 Iub links between NodeBs and RNCs. Over 27 million configuration parameters used in over 15,000 network elements from multiple equipment suppliers, spanning mobile and backhaul networks are collected, analyzed, and compared to gold-standard definitions. Analytics identifying parameter misconfigurations helps the mobile operator correlate customer experience trouble tickets and prioritize remediation actions.