article page
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | to proactively discover network issues and device incompatibilities as soon after product launch as possible - before such issues are discovered by a large number of new device owners.
With a CSA solution, the operator can continuously monitor customer service usage data that is tied to a select number of measurement parameters. The data is aggregated by mobile device make and model, which yields voice and data efficiency profiles by device type. Performance that falls below certain thresholds is flagged for additional analysis and verification. Examples of such measures include:
- Voice efficiency – ratio of number of successful calls to the total number of call attempts; commonly called answer-seize ratio (ASR).
- Voice effective calls – same as voice efficiency but excludes data pertaining to subscriber busy, subscriber no answer and release of call before answer.
- Short message service (SMS) efficiency – ratio of SMS delivered compared with the total SMS sent.
- Additional SMS – average number of SMS sent that are not successful on first delivery attempt (FDA) and the average number of retried delivery attempts.
- Email efficiency – number of emails sent and received by the user.
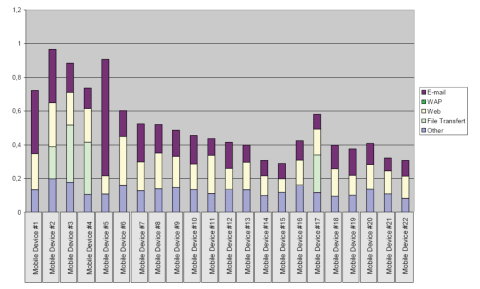
Summary charts that define user device measures are generated by the CSA solution to identify consistent, problematic, device-specific issues. Figure 1 displays service efficiency ratio by device type and service.
|
|
With a CSA solution, the operator can continuously monitor customer service usage data that is tied to a select number of measurement parameters. |
|


Once a problem has been identified, the operator can take of number of actions, including:
- Engagement with mobile supplier – The mobile phone supplier is contacted to work out an acceptable remedy to any identified network compatibility problem.
- Automatic customer notification – When problems are identified, an automatic device upgrade alert is sent directly to the subscriber explaining the issue and planned course of action.
- Automatic network alarm notification – Using international mobile equipment identity (IMEI) data, the operator sets alarms to identify when a device on the “notice for corrective action” list is connected to the network; thereby requiring special attention.
- Customer interaction alert – In certain circumstances, the SP contacts the customer to review the problem, going through a series of resolution procedures, including recommended usage behaviors, to help them have the best possible mobile device experience. In cases where a software patch, update or new configuration is available, it is offered to the customer via SMS and or email to trigger an automatic update. The operator may also prescribe special usage procedures to make sure subscribers have configured their equipment properly.
|
|
|
|
| |

article page
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|
|